Effective Ways to Find Horizontal Asymptote in 2025
Understanding Horizontal Asymptote and Its Definition
Besides being a fundamental concept in calculus, a **horizontal asymptote** is a line that represents the behavior of a function as it approaches infinity. It helps in analyzing the long-term trends of functions, especially **rational functions and asymptotes**. Essentially, a horizontal asymptote is defined mathematically in terms of limits; specifically, it indicates the value that a function approaches as the input values grow larger or smaller. For example, if a function’s value approaches a specific number as x approaches infinity or negative infinity, that number represents the horizontal asymptote of the function. Understanding **horizontal asymptote definitions** is crucial for students seeking to grasp the nuances of calculus and to solve **horizontal asymptote problems** effectively.
The Importance of Horizontal Asymptotes in Calculus
In calculus, understanding **horizontal asymptotes** allows for an accurate depiction of a function’s **end behavior**. These asymptotes provide significant insights when graphing functions, making them essential for solving calculus problems. By examining the horizontal asymptote, one can determine how a function behaves at extreme values, particularly whether it approaches a fixed value or continues indefinitely in one direction. When you analyze **limits and horizontal asymptotes**, you gain a deeper comprehension of the overall traits of a function, which aids in forecasting its graphical representation effectively.
Examples of Horizontal Asymptotes
To solidify the concept of horizontal asymptotes, let’s explore an example. Consider the function f(x) = (2x + 1)/(3x – 1). To find the horizontal asymptote, we examine the limits as x approaches infinity: lim (x→∞) f(x) = (2x + 1)/(3x – 1) = 2/3. Thus, the horizontal asymptote is y = 2/3, indicating that as x increases or decreases infinitely, the function approaches the line y = 2/3. This practical example illustrates the step-by-step approach to **calculating horizontal asymptotes**, making the process understandable.
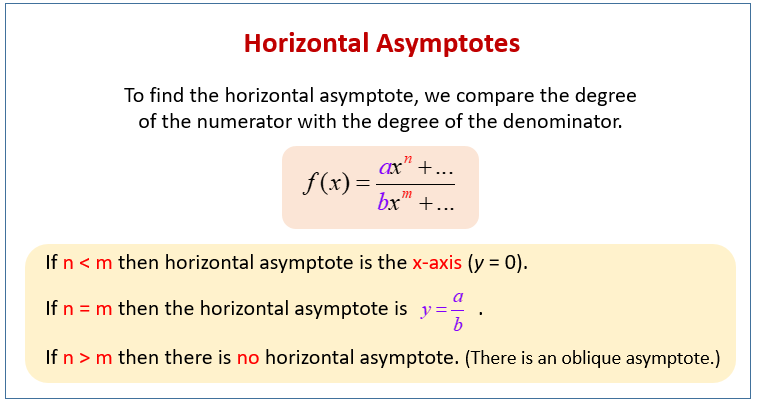
Techniques for Finding Horizontal Asymptotes
Identifying the horizontal asymptotes of a function is crucial for mathematical analysis. Here, we present various techniques that facilitate this understanding. The first and most straightforward method involves analyzing the highest degree of the polynomial in the numerator and denominator of a **rational function**. The general rules are as follows: if the degree of the numerator is less than that of the denominator, the horizontal asymptote is y = 0; if the degrees are equal, the asymptote equals the ratio of the leading coefficients; and if the degree of the numerator exceeds that of the denominator, there is no horizontal asymptote.
Applying Limit Analysis for Horizontal Asymptotes
Another effective technique for finding horizontal asymptotes is using limits. By applying the **limits at infinity**, one can evaluate the cases where x approaches positive or negative infinity. For instance, if you want to determine the horizontal asymptote of the function f(x) = 5x^3 + 2, you evaluate lim (x→∞) f(x). This approach reveals that the function increases without bound, indicating that **horizontal asymptotes** may not exist in this case. However, applying **limit analysis** is universally applicable whenever you’re tasked with understanding the long-range behavior of various functions.
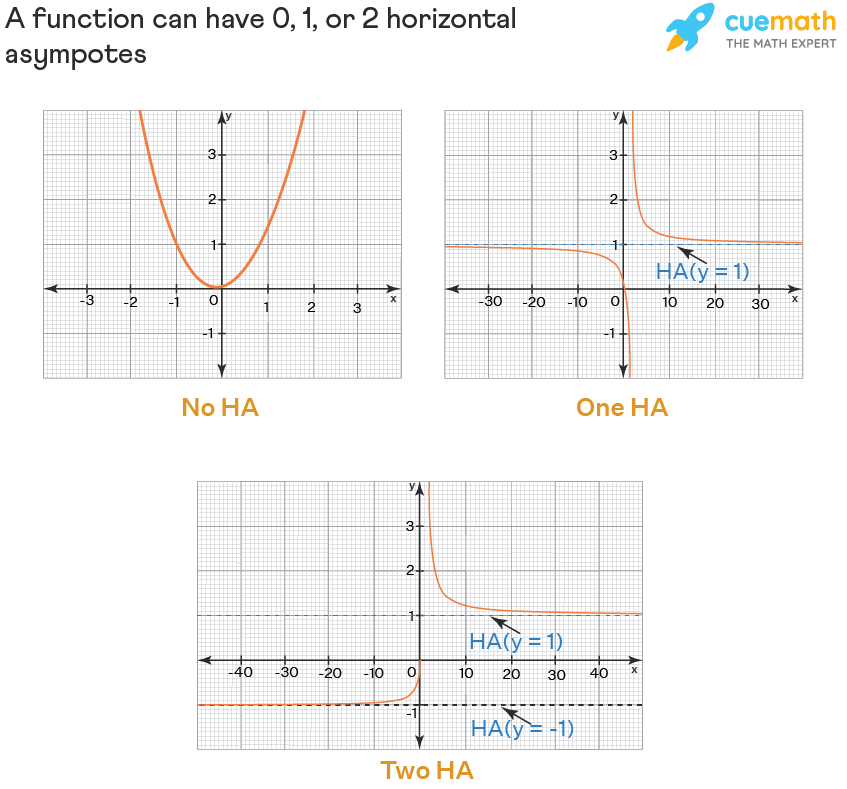
Graphical Visualization of Horizontal Asymptotes
Using a **horizontal asymptote graph** often enhances students’ understanding of asymptotic behavior. By graphing a function alongside its horizontal asymptotes, students can visually grasp how the function approaches these lines at the extremes. This illustrative technique fosters a more intuitive understanding and can significantly reduce errors in calculations of **horizontal line tests**. Whether working with polynomial functions or more complex **rational expressions**, developing skills in **graphing horizontal asymptotes** provides invaluable insights into the behavior of functions in calculus.
Common Mistakes in Identifying Horizontal Asymptotes
Despite understanding the rules and techniques, students often encounter common pitfalls when trying to identify horizontal asymptotes. A frequent mistake involves confusing horizontal asymptotes with vertical asymptotes. Remember, while horizontal asymptotes reveal a function’s behavior as it approaches infinity, vertical asymptotes indicate where the function is undefined. Another error is applying the rules hastily without fully analyzing the degrees of the numerator and denominator; giving superficial analyses can lead to incorrect conclusions. Therefore, practicing through **horizontal asymptote worksheets** can significantly enhance accuracy and comprehension.
Challenges When Identifying Horizontal Asymptotes
One of the challenges students face is calculations pertaining to complex functions. For instance, finding horizontal asymptotes when dealing with composite functions or when the contributing rational expressions have varying degrees can be tricky. In such cases, employing systematic approaches highlighting leading terms becomes necessary. Creating a checklist before conducting limit analyses helps catch possible miscalculations. Key aspects to look for include highest-degree terms, coefficients, and potential transformations that redefine function behavior. More attention on these elements ensures a robust grasp on the intricacies of deriving **horizontal asymptotes**.
Horizontal Asymptote Practice Problems
Practicing is essential in mastering how to find **horizontal asymptotes**. Educators can develop problem sets that tackle various functions, from simple polynomials to more complex rational expressions. For example, inquire about the horizontal asymptote of f(x) = (x^2 – 4)/(2x^2 + 3). In this case, both numerator and denominator have degrees of 2, suggesting the horizontal asymptote will be the ratio of leading coefficients, i.e., 1/2. Hands-on practice builds proficiency and firmly establishes the theoretical foundations of limits and rational expressions.
Conclusion on Understanding Horizontal Asymptotes
In conclusion, grasping the concept of **horizontal asymptotes** in calculus not only reinforces fundamental mathematical principles but also enhances analytical and problem-solving skills. The association between limits and horizontal behavior significantly helps in graphing functions reliably and making accurate predictions about their long-term behavior. By implementing techniques such as limit calculations, graphical analysis, and comprehensive practice, students can build on their knowledge and tackle complex calculus problems with confidence.
Key Takeaways
- Horizontal asymptotes indicate the behavior of functions as inputs approach infinity.
- Techniques include limit analysis and degree comparison for effective identification.
- Misunderstanding horizontal and vertical asymptotes can lead to common mistakes.
- Hands-on practice improves skills and reinforces conceptual understanding.
- Graphing functions alongside their asymptotes enhances comprehension of their behavior.
FAQ
1. What is the horizontal asymptote definition?
The **horizontal asymptote definition** refers to a line that a function approaches as its variable tends to infinity. It indicates the limiting value of the function for extreme values of its input, providing insight into the long-term behavior of the function.
2. How do you find horizontal asymptotes in calculus?
To find horizontal asymptotes in calculus, you can analyze the degrees of the numerator and denominator of a rational function and apply limits. For example, if the degree of the numerator is less than that of the denominator, the asymptote is y = 0.
3. What are some common vertical vs horizontal asymptote differences?
Vertical asymptotes indicate points at which a function is undefined, typically resulting from division by zero, whereas horizontal asymptotes show how a function behaves as it approaches infinity. Understanding these differences is fundamental to calculus.
4. Can you provide examples of horizontal asymptotes?
Sure! A common example is the function f(x) = (4x + 3)/(2x + 1). Here, the horizontal asymptote would be y = 2, calculated since both numerator and denominator have equal degrees, thus using the ratio of their leading coefficients.
5. Why are horizontal asymptotes significant in calculus?
Horizontal asymptotes are significant in calculus as they help predict the end behavior of functions. Being able to identify these lines provides deeper insight when constructing graphs and solving **horizontal asymptote challenges**.
6. What tools can be used for horizontal asymptote verification?
Tools such as **horizontal asymptote calculators** and graphing software can visually confirm the presence of horizontal asymptotes as well as compute limits to ensure accurate identification of their values in various functions.
7. What additional resources can assist with horizontal asymptotes?
Several educational platforms provide comprehensive courses and resources on understanding asymptotes in calculus. Online materials, including explanatory videos and interactive examples, provide a well-rounded approach to mastering the concept of horizontal asymptotes.